Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Chainlink
We've just announced IQ AI.
Chainlink
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that brings off-chain data into an on-chain format, bridging the gap between the isolated blockchain and real-world data.[1][2]
History
Chainlink was developed by Chainlink Labs (formerly Smart Contract Ltd.) and founded In September 2014 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis. It currently supports not only Ethereum, but also additional blockchains and layer 2 networks such as Polygon, BNB Chain, Avalanche, and Arbitrum. LINK is the native token of the protocol, which is secured by a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.[3]
On September 19, 2017, Chainlink raised USD 32,000,000 by selling over 350 million LINK tokens in an ICO (initial coin offering). Chainlink has partnered with various mainstream organizations like AccuWeather, FedEx, FlightStats, and the Associated Press. On October 21, 2021, The Associated Press partnered with Chainlink to make its trusted economic, sports and race call datasets available to leading blockchains. Also, IQ.wiki formerly Everipedia in partnership with the Associated Press, using the Chainlink infrastructure, published the results of the 2020 U.S. Presidential Elections onto the blockchain for the first time.[72]
On May 21, 2021, Chainlink Labs became the first crypto-native member of the Hedera Governing Council, which oversees Hedera Hashgraph's distributed governance. Hedera integrated Chainlink's decentralized oracle service into its Hedera Token Service (HTS) and endorsed it as the preferred oracle solution. [102]
On June 7, 2022, Chainlink Protocol announced information about its long-term objectives and new roadmap, which will usher in the "Chainlink Economics 2.0" era for the network. Chainlink will finally roll out staking for LINK holders to secure the network and earn rewards.
As of 2022, the Chainlink ecosystem presently has access to over 1 billion data points and manages over $75 billion in value through integrations with 1,000 projects across 700 oracle networks.[73][7]
On May 19, 2023, Chainlink and Arbitrum integrated Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) into Arbitrum One, a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. This collaboration enhances randomness security for applications on Arbitrum's platform, particularly benefiting NFT and gaming sectors. The integration aims to promote innovation and growth in decentralized applications, aligning with the increasing role of Layer 2 solutions in enhancing blockchain scalability and security. [104]
On July 17, 2023, Chainlink's Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), designed to facilitate cross-chain applications, went live for early access users on multiple blockchains, including Avalanche, Ethereum, Optimism, and Polygon. The protocol has undergone successful testing with over 25 partners, including prominent names like Aave and Synthetix from the decentralized finance sector. [101]
Overview
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that feeds a stream of data to smart contracts running on several blockchains. Its goal is to make smart contracts even more powerful by allowing them to use variable data from other sources.
Through Chainlink oracles, smart contracts can pull data from off-chain sources and bring it onto the blockchain. The innovative concept introduces new ways for smart contracts to be used. Prediction markets are just one example of how aggregating knowledge on-chain from trusted sources can add value to smart contracts while removing middlemen and uprooting traditional markets. Since blockchains are generally intended to operate as a “trustless” Network, using outside data requires integrating with a trusted source – an “oracle.” Through decentralization, the Chainlink network can verífy oracle integrity, order match, and aggregate results to ensure that all data being sourced is valid.[4]
Chainlink is designed to be modular and flexible and even allows smart contracts to be upgraded through a migration function.
Oracles
Oracles allow blockchains to access data outside of their network. They find and verify real-world occurrences through trusted sources, submitting the information to a blockchain to be used in smart contracts. The oracle provides external data that is necessary to execute pre-defined conditions within smart contracts.
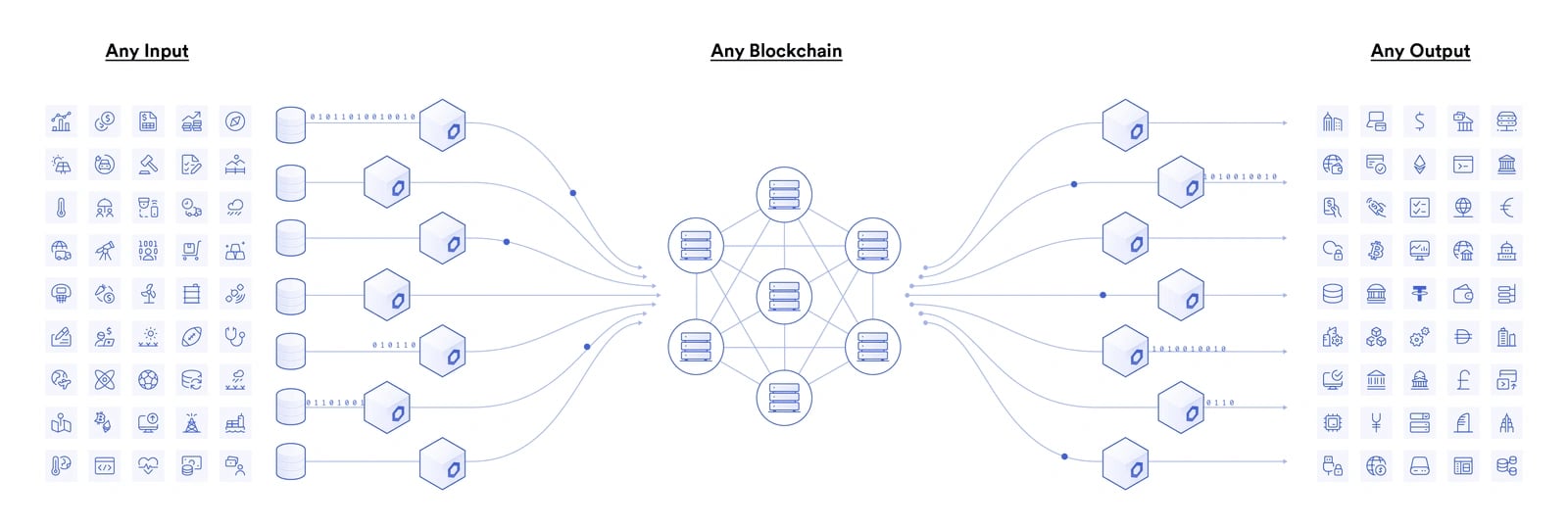
Use Cases
DeFi
Anyone can build a Defi app using Chainlink. It is the industry standard oracle network for DeFi. A decentralized finance ecosystem can be powered using Chainlink Decentralized Oracle Networks.
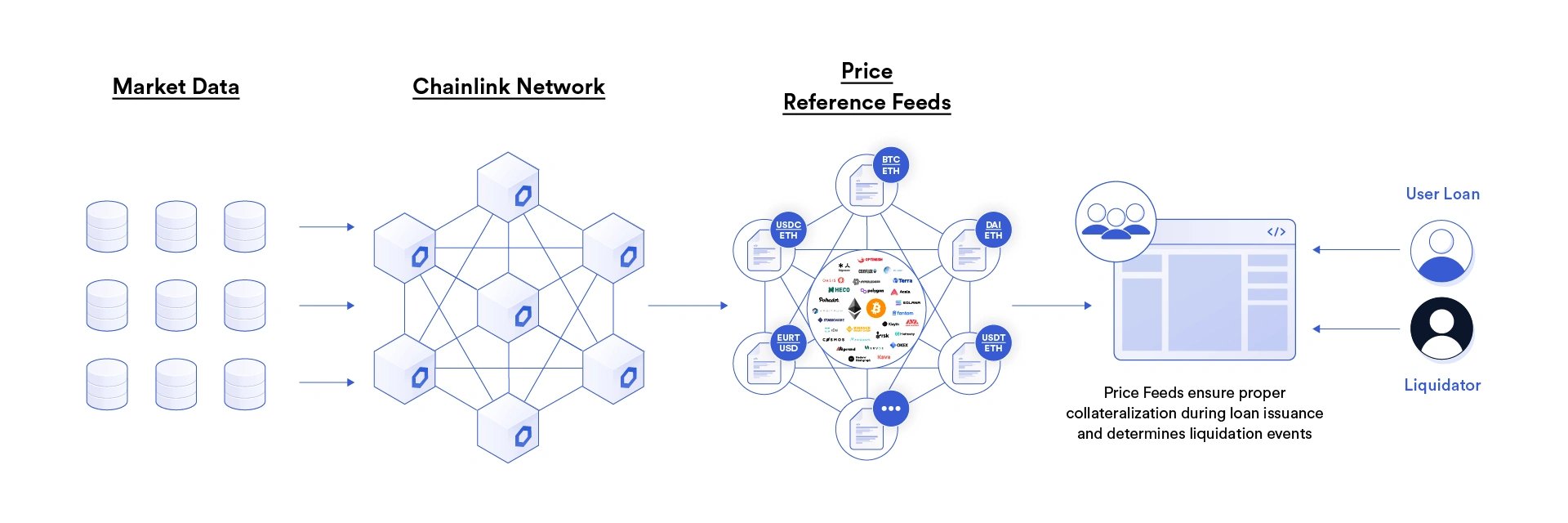
Chainlink also connects hybrid smart contracts with high-quality data and off-chain computation which it uses to help secure tens of billions of dollars within the DeFi ecosystem.
Chainlink offers a diverse range of decentralized services and Rapid integration and deployment of advanced DeFi applications. Some of its Integrated applications include:
Enterprise
Chainlink is the industry standard middleware for connecting enterprises to the blockchain economy. Its oracle infrastructure enables organizations to securely and easily connect their existing systems to all major blockchain networks.
Enterprises can now use Chainlink to generate new revenue streams by operating critical smart contract infrastructure in the form of a Chainlink node, providing hybrid smart contracts access to a secure source of real-world data and off-chain computation.
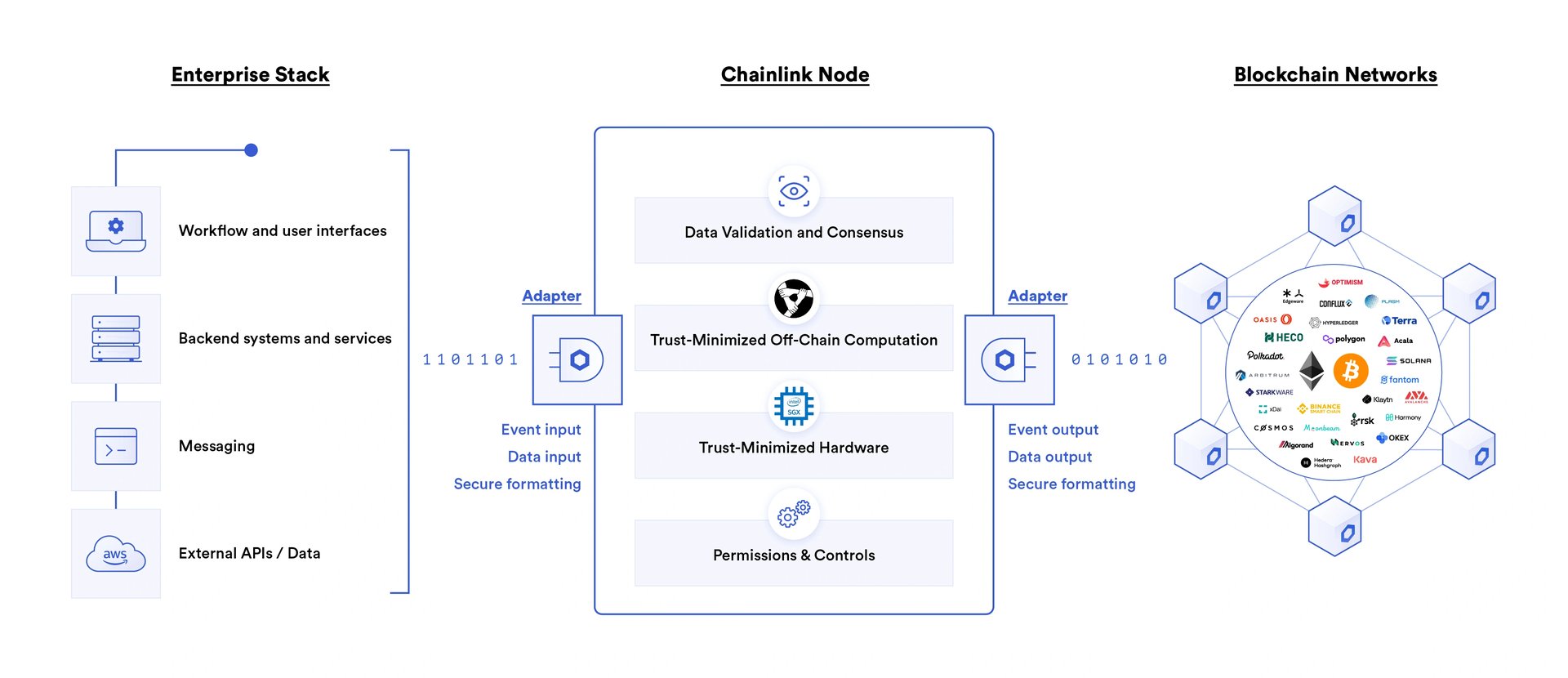
Examples of these enterprises using chainlink include LexisNexis, Swisscom, AccuWeather, and The Associated Press.
Insurance
Chainlink can also be used to power the next generation of blockchain-enabled insurance. Its Decentralized Oracle Networks securely provides blockchain-based insurance products access to real-world data and off-chain computation.
Chainlink can be used to design secure parametric insurance products/applications, help developers to monetize their data by selling it to blockchain-based insurance projects.[80]
NFTs and blockchain games
Chainlink also supports the integration of NFT and blockchain gaming projects. Its oracles power top NFT and gaming applications across the blockchain ecosystem, helping dApps provide users with dynamic and provably fair gameplay.
Users can confirm that their rare and unique digital assets are unique by using Chainlink to ensure that NFT minting, distribution, and trait assignment are done in a provably secure manner. It also brings secure entropy to blockchain games to randomize in-game parameters.
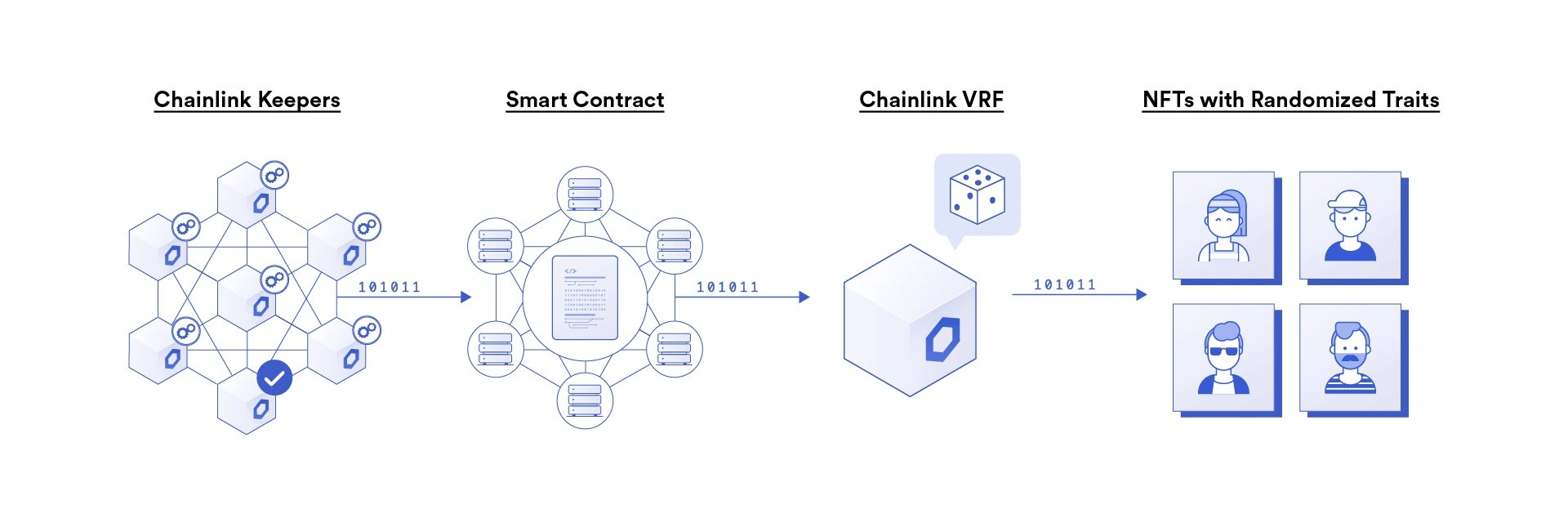
Social Impact
Chainlink helps promote blockchain innovations to bring about great social change. Through Chainlink, organizations, NGOs, businesses, and other institutions with a social conscience can harness the potential of smart contracts to advance financial inclusion, environmental sustainability, and the common good.
Climate Markets
Chainlink is known for being the industry standard for on-chain climate data, which it offers to its users. Enterprise-grade middleware, provided by the Chainlink Network, enables high-integrity, interoperable, and effective climate markets.[82]
The Chainlink Network connects carbon markets and helps bring transparency to the measuring and tracking of climate commitments.
Chainlink Token (LINK)
The LINK token is an ERC-20 token, with the additional ERC-223 “transfer and call” functionality of transfer (address, uint256, bytes), allowing tokens to be received and processed by contracts within a single transaction. To compensate for the off-chain needs of the Chainlink system, the LINK token has been established as the currency of choice to pay Node Operators.
According to the developers, the LINK token is required to perform this function, with the demand and value of the tokens being directly correlated to the number of operators that offer off-chain services to the system. As LINK tokens are used as a currency on the Chainlink platform, the more usage the Chainlink platform has, the more valuable LINK tokens should be.[5]
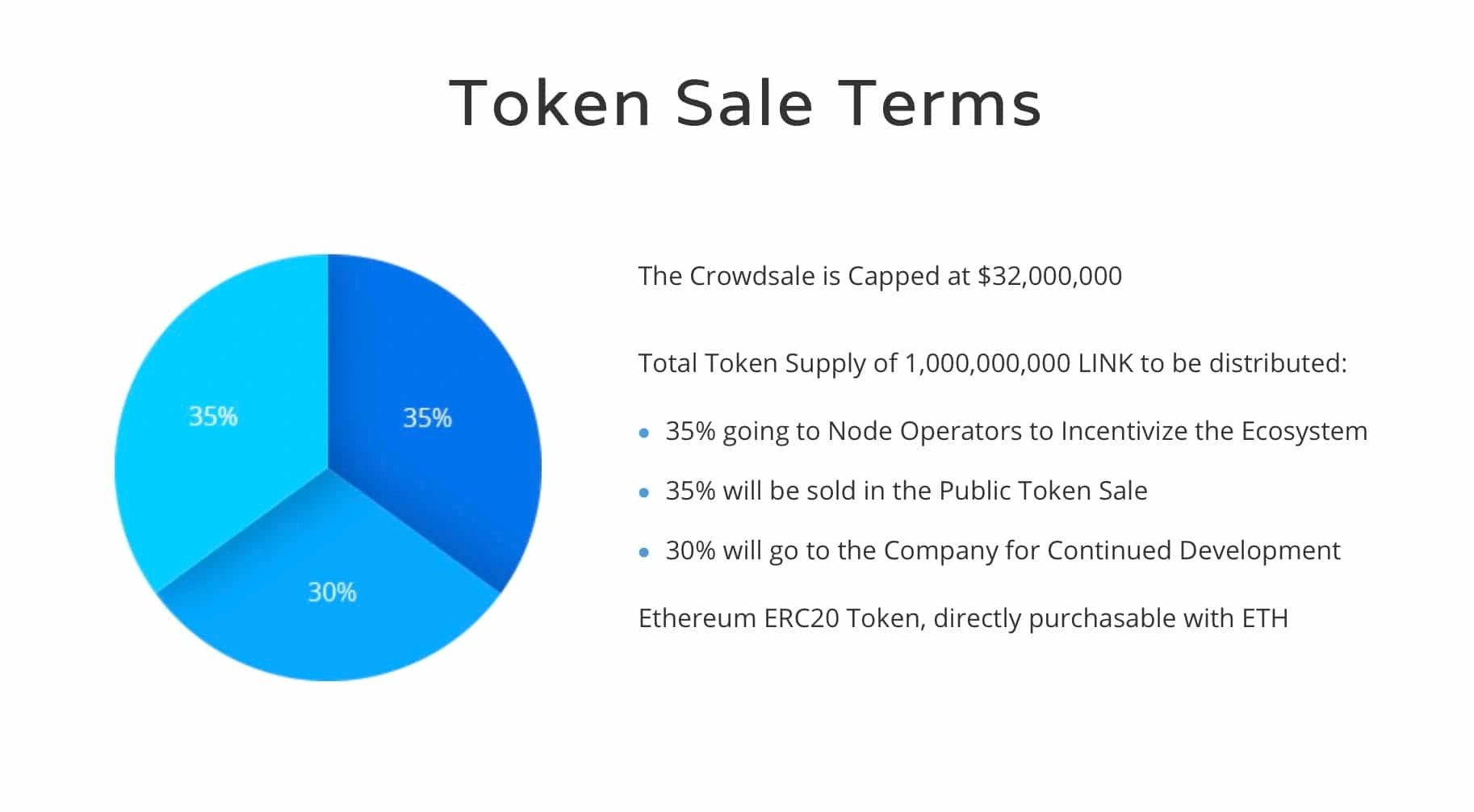
The LINK token has a total supply of 1,000,000,000 LINK tokens.
Token Distribution
The initial coin offering (ICO) took place in September 2017 and a total of 350 million LINK tokens were sold to investors at $0.11 per token. 35% of the total token supply will go towards node operators and the incentivization of the ecosystem. Another 35% of LINK tokens were distributed during public sale events. Lastly, the remaining 30% of the total token supply was directed towards the company for the continued development of the Chainlink ecosystem and network.[74][75]
Uses
- Internal Payment
This is the currency used to pay the Chainlink node operators for their work.
- Staking
Chainlink node operators have to stake in the network to participate and provide data services. Nodes with higher stakes have a higher chance of getting selected to provide the requested data.
Ecosystem
A large open-source community of data producers, node operators, smart contract developers, researchers, security auditors, and other professionals powers Chainlink Ecosystem.
Data Providers
Data providers sell their existing data and API services to the most widely used oracle networks, quickly expanding their business model into the emerging smart contract economy with minimal costs. Data providers can monetize their current infrastructure and concentrate entirely on delivering high-quality data since Chainlink takes away all the difficulties associated with managing nodes and processing cryptocurrency payments.
Node Operators
At the core of the Chainlink, Network is the Chainlink node operators, they administer and maintain the oracle infrastructure necessary to give every blockchain's smart contracts safe access to the best real-world data.
Node Operators earn revenue by roviding oracle computation directly to smart contracts across any blockchain and running critical data infrastructure required for blockchains success.[76]
ChainLink Products
Market and Data Feeds
Chainlink Provides decentralized and high-quality data feed for DeFi, Sports, Weather, and many more. These Data Feeds provide a secure, reliable, and decentralized source of off-chain data to power unique smart contract use cases for DeFi and beyond.
NFT Floor Pricing Feed
Chainlink NFT Floor Pricing Feeds offers an estimate of the floor price for a particular NFT collection. These feeds function similarly to other Chainlink Data Feeds and utilize Coinbase Cloud's aggregation algorithm and Chainlink's oracle infrastructure to eliminate extreme price deviations and protect against market manipulation. NFT Floor Pricing Feeds can be utilized in a variety of applications that require accurate NFT data, such as lending and borrowing, on-chain derivatives, dynamic NFTs, gaming guilds, CeFi products, prediction markets, and more.[94]
The first collections supported by these feeds are Azuki Official, Bored Ape Yacht Club, CloneX, Cool Cats, CrypToadz, CryptoPunks, Doodles, Mutant Apes, Vee Friends, and World of Women. These feeds serve to bridge the gap between the DeFi and NFT economies, enabling the creation of new financial products and services powered by Chainlink's trusted oracle infrastructure. The NFT Floor Pricing Feeds can be used in a variety of use cases, including lending and borrowing, on-chain derivatives, dynamic NFTs, gaming guilds, CeFi products, and prediction markets.[95]
Chainlink's NFT price feeds provide smart contracts and applications with access to market data from multiple NFT marketplaces through a decentralized oracle network. The price data is generated by collecting market data from various sources, analyzing it using Coinbase Cloud's data analysis tools, and delivering the resulting data to smart contracts and applications. [96]
VRF (Verifiable Random Function)
Chainlink provides a verifiable, tamper-proof random number generator for blockchain gaming and NFT projects. Chainlink VRF aims to be a secure and fair random number generator for smart contracts. It produces random values along with cryptographic proofs that validate their authenticity. These proofs are verified on the blockchain before being used, ensuring that the generated randomness is tamper-proof and trustworthy. This feature is valuable for applications that require unpredictable outcomes, such as blockchain games, NFTs, assigning tasks, selecting samples, and more. There are two ways to request randomness: through a subscription account funded with LINK tokens or by directly funding the random value requests with LINK tokens. [103]
Automation
Chainlink also provides reliable, high-performance, decentralized automation for smart contracts. Its automation enables Web3 developers to seamlessly automate key smart contract functions in a decentralized manner.
Chainlink Automation allows for the conditional execution of functions within smart contracts through the use of a decentralized and highly reliable automation system. It utilizes the same external network of node operators that is responsible for securing billions of dollars in value. Using Chainlink Automation can help a user get their product to market more quickly, while also avoiding the costs and risks associated with a centralized automation stack.[91]
Proof of Reserve
Chainlink gives its users autonomous, reliable, and timely audits of on-chain and off-chain reserves. Its Proof of Reserve enables the reliable and timely monitoring of reserve assets using automated audits based on cryptographic truth.
Cross-Chain Communication (CCIP)
With Chainlink, users can build cross-chain applications quickly and with ease. With the help of the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), programmers may create safe services and applications that can transmit messages, transfer tokens, and start activities across many network. CCIP was launched with the collaboration with SWIFT, the bank-focused closed network for international money transfers. In line with this collaboration, CCIP will be utilized to connect SWIFT with diverse blockchain networks. The ongoing initiative holds the potential to establish connections between multiple blockchains and bank chains, as emphasized by Chainlink co-founder Sergey Nazarov. [101]
Architecture
Requesting Contract and Requesting Interface
Chainlink acts as a secure blockchain middleware and decentralized oracle network that brings external data onto the blockchain. ChainLink nodes return replies to data requests made by user contracts which consist of a requesting contract, signified by USER-SC, and a requesting interface signified by CHAINLINK-SC. The requesting interface is comprised of three main contracts a reputation contract, an order-matching contract, and an aggregating contract.[11]
- The reputation contract keeps track of oracle-service-provider performance metrics to inform whether or not an oracle-service provider is trustworthy not
- The order-matching contract takes a proposed service level agreement and collects bids from oracle providers.
- The aggregating contract collects the oracle providers’ responses and calculates the final collective result of the ChainLink query.
Off-Chain Architecture
Chainlink consists of a network of oracle nodes connected to the Ethereum network that independently harvests responses to off-chain requests. The individual responses are aggregated into a global response that is returned to the requesting contract, USER-SC. The two main components in the off-chain architecture are:
- ChainLink Core: Work done by Chainlink nodes is formatted assets of job specifications known as subtasks. Each subtask has a specific operation it performs, before passing its result onto the next subtask, and ultimately reaching a final result. Subtasks include, but are not limited to, HTTP requests, JSON parsing, and conversion to various blockchain formats.
- External Adapters: Custom subtasks can be defined by creating adapters. Adapters allow programs in any programming language to be easily implemented simply by adding a small intermediate API in front of the program. Chainlink uses a schema system based on JSON to specify what inputs each adapter needs and how they should be formatted.[76][77]
Chainlink Workflow
- USER-SC makes an on-chain request.
- CHAINLINK-SC logs an event for the oracles.
- ChainLink core picks up the event and routes the assignment to an adapter.
- ChainLink adapter performs a request to an external API.
- ChainLink adapter processes the response and passes it back to the core.
- ChainLink core reports the data to CHAINLINK-SC.
- CHAINLINK-SC aggregates responses and passes them back as a single response to USER-SC.
In-Contract Aggregation
Decentralization is a key part of Chainlink's security. Aggregating data from distributed sources in the contracts allow for CHAINLINK-SC to gain a high degree of trust. To ensure the integrity of the network, Chainlink fends off possible freeloaders with a commit and reveal algorithm. The algorithm prompts oracles to send CHAINLINK-SC cryptographic commitments to their responses. After CHAINLINK-SC has received a quorum of responses, it initiates a second round in which oracles reveal their responses. The sequential protocol with a delay between the commit and reveal prevents oracles from copying one another or, freeloading.
Off-Chain Aggregation
Chainlink proposes the use of threshold signatures to aggregate data off-chain. Such signatures can be implemented easily with Schnorr signatures. Oracles have a collective public key pk and a corresponding private key sk that is shared among O1, O2,..., On in a (t, n)-threshold manner. Such a sharing means that every node Oi has a distinct private/public key pair (ski , pki ).
O1 can generate a partial signature that can be verified concerning pki . This allows partial signatures on the same value A to be aggregated across any set of t oracles to yield a single valid collective signature on an answer A. To fight against bad actors in the system, a smart contract that doles out financial incentives in the form of LINK token rewards only oracles that have sourced original data for their partial signatures.[2]
Chainlink 2.0
On June 7, 2022, Chainlink Protocol announced information about its long-term objectives and new roadmap, which will usher in the "Chainlink Economics 2.0" era for the network.[68][69]
Chainlink 2.0 will enable the creation of hybrid smart contracts, which can access off-chain resources. In addition, the new system will facilitate oracles to “arbitrate off-chain oracle disputes.” Scalability and security are two of the new update's main advantages.
Scaling is possibly the most significant by-product of the new system. With hybrid contracts and off-chain computing, blockchains will achieve higher scalability due to constricted on-chain loads. As a result, the decentralized oracles will have higher throughput and low latency. Moreover, security will improve considerably with the use of super-liner staking, which makes manipulation doubly difficult.
All in all, the new system provides unmatched guarantees to its users concerning the veracity, availability, and security of sourcing off-chain data.
On August 25, 2022, Chainlink Labs hosted the first-ever Twitter Spaces town hall with Chainlink co-founder Sergey Nazarov, who began by thanking the Chainlink community for playing a crucial part in the creation of Chainlink as the industry-standard decentralized oracle network.[68]
He further explained the importance of Chainlink becoming the top provider of Oracle network-based computation, securing tens of billions of dollars in DeFi, and how this accomplishment paves the way for Chainlink Economics 2.0.
“The goal of the Chainlink Economics 2.0 system is to make Chainlink itself sustainable for decades or into perpetuity and to tie that sustainability and that economic growth to the greater value secured by the industries in which Chainlink is a standard.” according to Sergey Nazarov.[69]
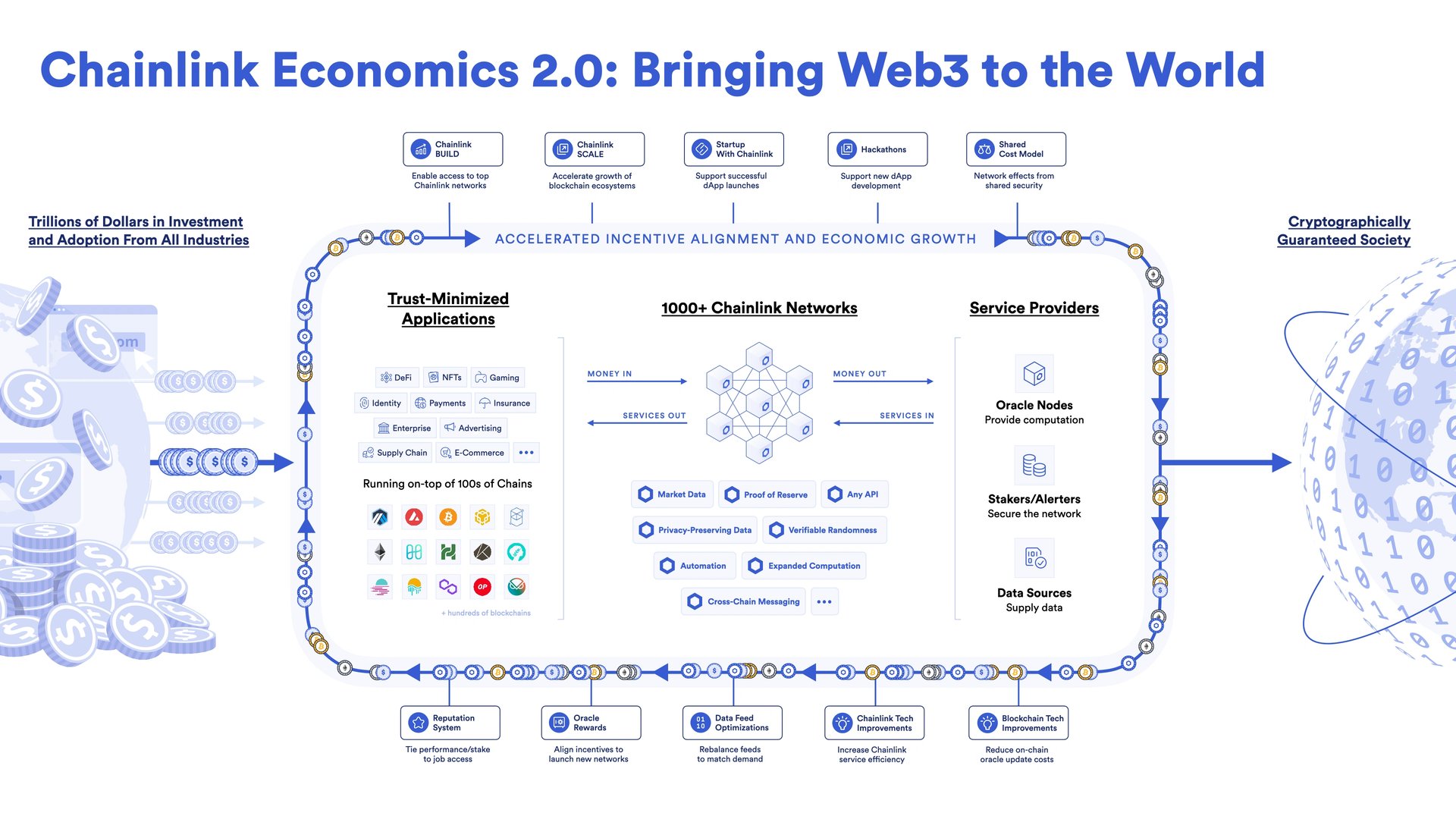
Chainlink Economics 2.0
Chainlink's Economics 2.0 consists of programs focused on:
- Increasing user fees paid to Chainlink service providers
- Reducing the on-chain & operating costs of oracle services
- Enabling a broader scope of service providers such as stakers to participate in the ecosystem.[86]
Staking v0.1
Staking LINK marked the start of the Economics 2.0 era, bringing "long-term security and sustainability."
According to the announcement released by Chainlink, the overarching goal of staking on the network is to give ecosystem participants, including node operators and community members, the ability to increase the security guarantees and user assurances of oracle services by backing them with staked LINK tokens.
By staking LINK, the ability for nodes to receive jobs and earn fees on the Chainlink network will be enhanced while the ecosystem as a whole will benefit from an increase in crypto-economic security and user assurances.
Staking not only introduces an incentive to provide reliable data, but it allows for a penalty mechanism for underperforming nodes who fail to achieve the goal of consistently generating accurate oracle reports and delivering them to specific destinations on time.[2][3]
The beta version went live on Ethereum mainnet on December 6, 2022. It consists of a staking pool that supports the ETH/USD Data Feed on the Ethereum mainnet.
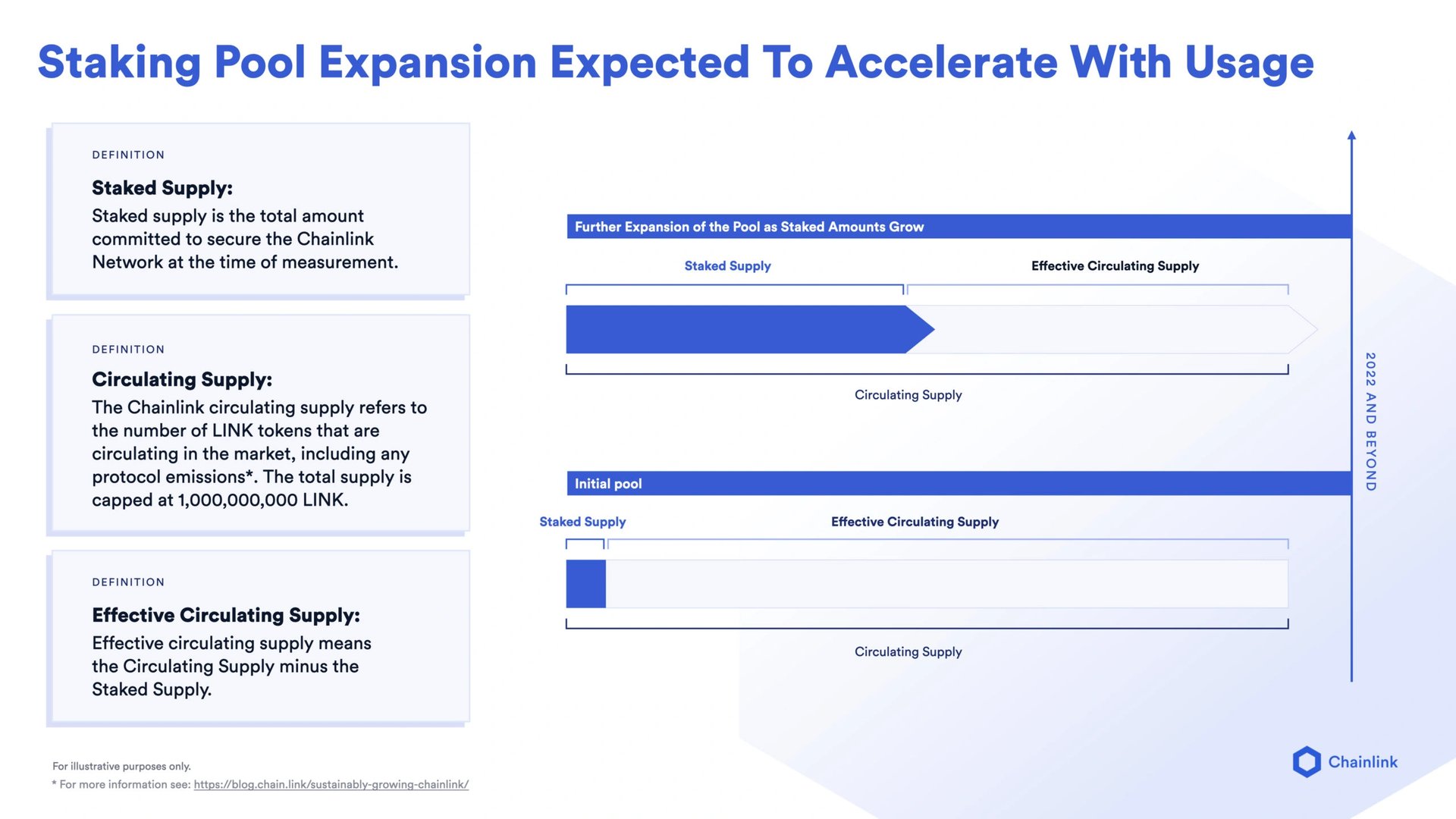
Stakers will earn rewards by participating in a decentralized alerting system that monitors the Data Feed's uptime. The staking pool will initially be capped at 25 million LINK, representing 5% of the current circulating supply and 2.5% of the total supply. The pool will initially have two types of stakers: Node Operator Stakers and Community Stakers. A fair-entry mechanism has been created to determine which community members get access to the limited pool space. Once the beta version is launched, 22.5 million LINK will be allotted for Community Stakers on a first-come-first-serve basis, while 2.5 million LINK will be allotted and reserved for Node Operator Stakers. The proportional difference between different staking allotments may be adjusted in the future to enhance the security of the pool.[92][93]
BUILD Program
BUILD is Chainlinks' new Economics 2.0 program accelerating the growth of Web3 projects. By granting greater access to Chainlink services and technical support in exchange for guarantees of fees and other incentives to Chainlink service providers, such as stakers, it intends to hasten the growth of early-stage and established enterprises inside the Chainlink ecosystem.[87]
SCALE Program
SCALE which stands for Sustainable Chainlink Access for Layer 1 & 2 Enablement, is also a part of the Chainlink Economics 2.0 program. It is meant to accelerate the growth of on-chain ecosystems by blockchains/L2s helping cover the costs of Chainlink oracles supporting their dApps.
For both blockchains and the Chainlink Network, SCALE is an all-encompassing and beneficial economic model.
Fees from dApps can eventually pay the full on-chain costs of Chainlink oracle nodes, enabling long-term viability across many ecosystems as L1 & L2 userbases grow. The following projects are one of the first to participate in the Chainlink SCALE program: Avalanche, Metis, Moonbeam, and Moonriver Network.[88][89]
Partnerships and Collaboration
Chainlink has an extensive list of partnerships, including [47][12][13]
- Credits[14]
- Oracle[15]
- V Systems[16]
- DApps Inc[17]
- Google Cloud[18]
- Matic
- GoChain[19]
- Reserve[20]
- Harmony[21]
- Shyft[22]
- Hedera Hashgraph[23]
- IOST[24]
- Streamr[25]
- Ocean Protocol[26]
- Synthetix[27]
- Provable[28]
- Celer[29]
- STK[30]
- Mobilum[31]
- ETHA[32]
- Kaiko[33]
- Wanchain[34]
- Hydrogen[35]
- bZx [36]
- Morpheus Network (MRPH)[37]
- Web3 Foundation[38]
- GameDex[39]
- Openlaw[40]
- OpenZeppelin[41]
- ClinTex[42]
- BET Protocol
- Binance[43]
- Ethereum Classic[44]
- Chillz[45]
- Etherisc[46]
- Swipe[47]
- 0x[48]
- Arbitrum[49]
- QAN Platform
- Cypherium[50]
- Contentos[51]
- Bloom[52]
- IRISnet[53]
- Tezos[54]
- Totle[55]
- IQ.wiki
Chainlink X SWIFT
On September 28, 2022, chainlink announced via its Twitter account it will be partnering with SWIFT, an interbank messaging system, to bridge the gap between traditional and digital assets for TradFi institutions, accelerating the adoption of distributed ledger blockchains and benefiting various institutions across capital markets.[83]
SWIFT is using the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) as an initial proof of concept. CCIP will enable SWIFT messages to instruct on-chain token transfers, helping the SWIFT network become interoperable across all blockchain environments.[84]
Further coorperation
In June 2023, Chainlink and Swift announced their aim to improve connectivity between various blockchain networks. Notable financial institutions like DTCC, ANZ, BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, Citi, Clearstream, Euroclear, and Lloyds Banking Group joined the effort. The objective is to explore how Swift's infrastructure can enable seamless tokenized asset transfers across different blockchains. Chainlink's role includes enhancing connectivity across public and private blockchains, fostering real-world interoperability. This initiative addresses the challenge of fragmented tracking of tokenized assets across diverse networks. By establishing links, financial institutions aim to streamline operations, reduce friction, and improve asset management efficiency. [99][100]
“In such a highly fragmented ecosystem, it would simply not be feasible for financial institutions to connect to each and every platform individually. Overcoming this fragmentation will be key to the long-term scalability of the market.” - Tom Zschach, CIO at Swift.
Chainlink X Coinbase Cloud
On September 28, 2022, Chainlink announced its partnership with Coinbase Cloud to launch NFT Floor Pricing Feeds. This will allow developers to deploy unique smart contracts across DeFi use cases and more with high-quality pricing data and an optimal liquidity profile.[85]
Chainlink X IQ.wiki formerly Everipedia
In November 2020, The Associated Press used the IQ.wiki formerly Everipedia OraQle, which uses Chainlink infrastructure, to publish the results of the 2020 U.S. Presidential Elections onto the blockchain for the first time. [56]
Daniel Kochis, head of business development at Chainlink spoke about the historic event:
“Making this powerful technology more accessible is key to realizing its full potential. And publishing the AP’s electoral race calls onto the blockchain for the first time is a big milestone in that journey.”[57]
Chainlink X Google Cloud
In August 2021, Chainlink released a fully decentralized weather data feeds through a partnership with Google Cloud.
Chainlink X Arbitrum
Arbitrum, the most popular Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum dApp development, and Chainlink, the leading provider of oracle services, announced the release of Chainlink Automation on Arbitrum One. Developers can build sophisticated dApps with reliable and efficient automation thanks to the availability of a decentralized network of nodes that can monitor smart contracts and execute functions using Chainlink's transaction manager. This transaction manager, which has been extensively tested, handles nonce management, gas spikes, and network reorganizations.[97]
Chainlink x TrueUSD
TrueUSD has announced that it will utilize Chainlink Proof of Reserve to programatically manage minting and become the first USD-backed stablecoin to do so. This will allow for automatic verification of USD reserves to ensure that new TUSD is sufficiently collateralized. The reserves data for TUSD is aggregated by The Network Firm LLP (TNF), an independent accounting firm in the U.S., and is delivered on-chain via Chainlink for use by the TUSD smart contract. [98]
“We’re excited to be using Chainlink Proof of Reserve to enhance the transparency and verifiability of our stablecoin. As the industry-standard decentralized oracle network, Chainlink helps ensure that TUSD is always collateralized by off-chain fiat reserves, furthering TUSD’s commitment to trust and transparency.” - Ryan Christensen, CEO of Archblock (the issuer of TUSD, formerly known as TrustToken)
ChainLink Marines and Memes
The group of passionate ChainLink enthusiasts who work tirelessly to push the product to mass adoption is known as ChainLink Marines. By April 2020 48,000+ addresses were holding between 100 and 10,000 LINK.[58]
In August 2020, the Link Marines rejected a report by Zeus Capital that called the project vaporware and warned that ChainLink would fall to as low as $0.07.[59] ChainLink was compared to Wirecard and Theranos which came crashing down in September of 2018. Another tweet on the Zeus Capital page claimed that Link Marines are paid to continue pumping the digital asset. Additionally, their ultimate goal is to take the money of unknowing investors.[60]
Memes are a major part of the ChainLink community and Pepe the Frog is used as an unofficial mascot. Some Link Marines buy and sell ChainLink meme NFTs on Opensea.
Chainlink God is among one of the most popular personalities on Crypto Twitter.
Celebrities
Kris Humphries
NBA player Kris Humphries is an investor and advocate for ChainLink. He first started tweeting about ChainLink in April 2020 and calls it a long-term play. In an interview with CryptoSlate, Kris Humphries explained that one of the factors that drove him to invest in and evangelize ChainLink was his understanding of the value of data as an NBA player and relating that to how ChainLink's value comes from putting off-chain data onto the blockchain.[61][62]
“Over the course of my time in the NBA, I witnessed the increasing role that data played in developing plays and overall team strategy. Anyone who follows the NBA has witnessed the evolution toward increased threes and attacking the net. This perspective helped me understand the value of data and shaped the types of projects I like in the blockchain space, including Chainlink.”
The other factor that drove him to invest was seeing ChainLink's team's strong work ethic and history of getting things done.[63]
“Coming into the NBA I told myself I would outwork everyone, then I met Dirk Nowitzki. He shifted my understanding of what it meant to grind and also the payoffs for doing so, especially when the stakes are high. In the early days of Chainlink, it was a small team of talented individuals who kept their heads down focusing on the technical components. Even during the 2017-2018 boom-bust when other projects were making flashy videos and hiring celebrities, I don’t even think Chainlink had a marketing team. That hard work and focus are now paying off.”
David Portnoy
In August 2020, David Portnoy announced that he had invested $250,000 worth of Bitcoin and United States dollars into ChainLink's LINK token. He also tweeted "$link to the moon," on August 15, 2020, to his 1.7 million followers. On August 21, 2020, Portnoy announced that he had sold all of his cryptocurrency after losing $25,000.[64][65][66][67]
Team & Advisors
- Sergey Nazarov - Chief Executive Officer
- Steve Ellis - Chief Technology Officer
- Dimitri Roche - Software Engineer
- Alex Kwiatkowski - Software Engineer
- John Barker - Software Engineer
- Dan Kochis - Global Head of BD & Partnerships
- Adelyn Zhou - Director of Marketing
- Brendan Magauran - Director of Operations
- Thomas Hodges - Integration Engineer
- Rory Piant - Community Manager
- Ari Juels - Technical Advisor
- Andrew Miller - Technical Advisor
- Evan Cheng - Technical Advisor
- Tom Gonser - Advisor
- Hudson Jameson - Technical Advisor
- Jake Brukhman - Advisor
- Brian Lio - Advisor[1]
See something wrong?
