订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Blockcha in Technology
Blockcha in Technology
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant record-keeping of digital transactions. This system has gained significant attention since its introduction as the underlying technology for Bitcoin in 2008, and has since found apps across various industries beyond cryptocurrency.
Overview
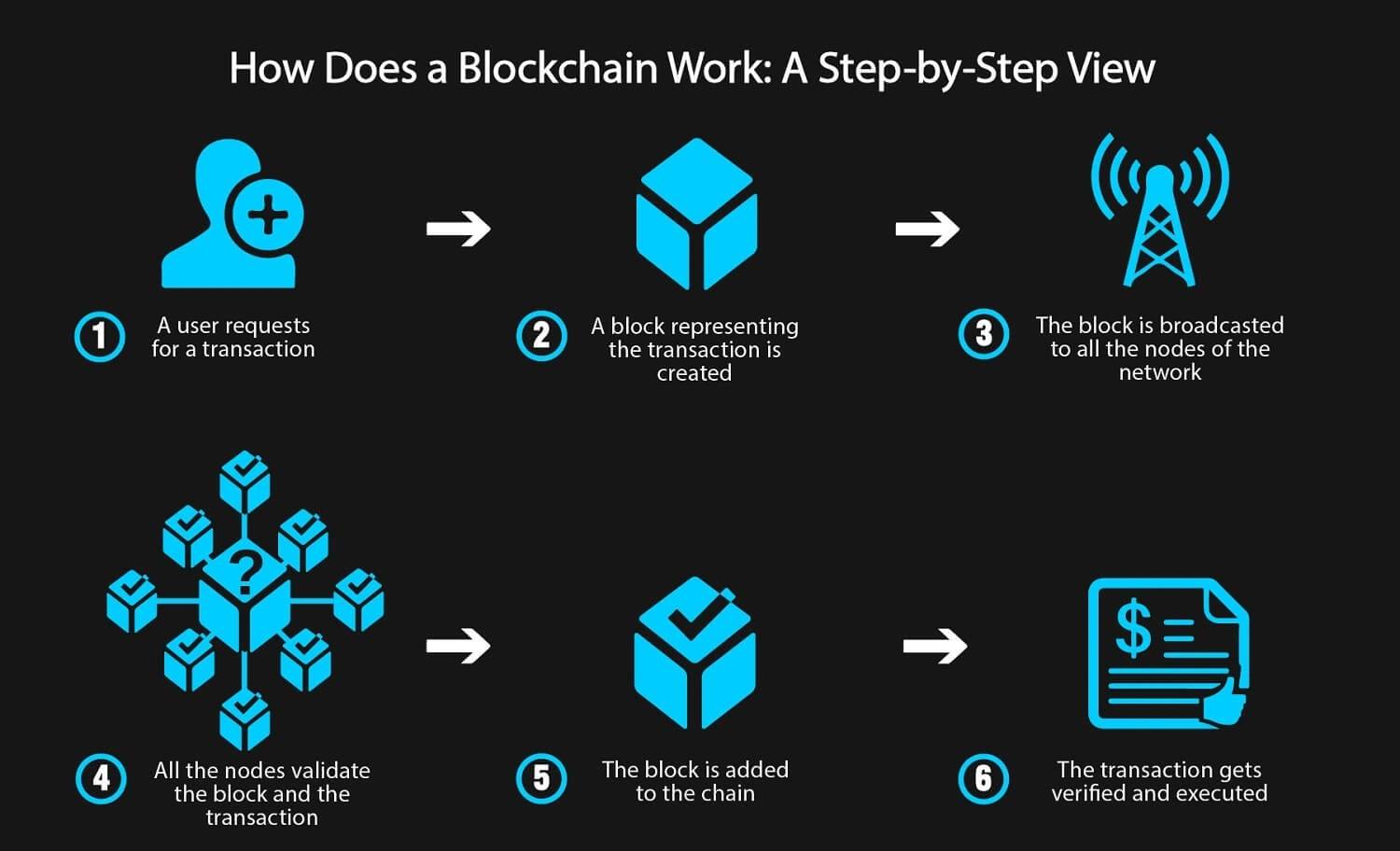
Blockchain technology functions as a decentralized database that records transactions in a series of linked blocks, secured by cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data, ensuring data integrity and transparency. Introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto in the whitepaper "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" [1], blockchain was initially developed for cryptocurrencies but now extends to finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more.
Key Features
Blockchain technology is characterized by several key features that contribute to its uniqueness and potential:
- : Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries and central authorities.
- : All transactions on a blockchain are visible to all participants, ensuring a high level of transparency.
- : Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or delete, ensuring data integrity.
- : Cryptographic techniques are used to secure transactions and control access to the blockchain.
- : Various algorithms (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake) are used to validate transactions and maintain network agreement.
- : Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, automating and enforcing the execution of contracts.
Types of Blockchain
Blockchains can be categorized into three main types:
- : Open, permissionless networks where anyone can participate in the consensus process. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- : Permissioned networks where participation is restricted to approved entities. Often used in enterprise settings.
- : Partially decentralized systems where the consensus process is controlled by a pre-selected group of nodes.
Applications
Blockchain technology has found applications across various industries:
Finance and Banking
- Cryptocurrencies and digital assets
- Cross-border payments and remittances
- Trade finance and supply chain financing
Supply Chain Management
- Product traceability and authenticity verification
- Inventory management and logistics optimisation
Healthcare
- Secure sharing of patient records
- Drug traceability and counterfeit prevention
Government and Public Sector
- Voting systems
- Land registry and property records
Energy Sector
- Peer-to-peer energy trading
- Renewable energy certificates
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
- : Many blockchain networks struggle with transaction speed and volume as they grow.
- : Proof of Work consensus mechanisms, in particular, require significant computational power and energy.
- : The legal and regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving in many jurisdictions.
- : Different blockchain networks often struggle to communicate and share data effectively.
Future Developments
The blockchain space is rapidly evolving, with several promising areas of development:
- : Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos aim to create interconnected blockchain ecosystems.
- : Layer 2 solutions and new consensus mechanisms are being developed to address scalability issues.
- : Many countries are exploring blockchain-based digital versions of their national currencies.
- : The growth of decentralized financial services built on blockchain platforms.
- : Unique digital assets representing ownership of digital or physical items.
As noted by Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum:
"Blockchain solves the problem of manipulation. When I speak about it in the West, people say they trust Google, Facebook, or their banks. But the rest of the world doesn't trust organizations and corporations that much — I mean Africa, India, the Eastern Europe, or Russia. It's not about the places where people are really rich. Blockchain's opportunities are the highest in the countries that haven't reached that level yet." [2]
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a paradigm shift in how we approach data management, trust, and decentralization. While it has already made significant impacts in various sectors, its full potential is yet to be realized. As the technology matures and overcomes current limitations, it is likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the digital landscape of the future.
[1] Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. [2] Buterin, V. (2017). Interview with ForkLog.
发现错误了吗?